WASHINGTON (AP) — President Barack Obama has signed into law the USA Freedom Act, which extends three expiring surveillance provisions of the 9/11-era USA Patriot Act. It also overhauls the most controversial provision, which had been interpreted to allow bulk collection of U.S. phone records by the National Security Agency.
Questions and answers about the bill the Senate passed on Tuesday and the House approved earlier:
What happens with the phone records collection?
It will resume for six months, provided that the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court orders phone companies to turn over the records and that no court stops it under various pending lawsuits. During that period, the NSA will seek to work with providers to come up with a way to quickly query their records against known terrorist phone numbers, pursuant to a court order. It will be able to collect data for all the numbers in contact with the suspect number, and all the numbers in contact with those numbers. So the NSA will still be rooting around in Americans’ phone records, but it won’t be collecting all of them. As for the American calling records the NSA has been collecting for years, Obama administration officials have not said what they will do with those and whether they will continue to search them.
What about the other surveillance provisions that expired?
The roving wiretap provision, which allows the FBI to eavesdrop on espionage and terror suspects who discard cell phones frequently, will go back into effect, as will the lone-wolf provision, which has never been used. The FBI will still be able to use Section 215 of the Patriot Act to collect a variety of business records in national security investigations. But the new law requires the government to limit the scope of its collection, prohibiting it from grabbing, for example, all information relating to a particular service provider or area code.
What else will change under the USA Freedom Act?
The new law gives private companies more leeway to publicly report information about the number of national security surveillance demands they receive. And it requires declassification of FISA Court opinions containing significant legal decisions, or a summary if declassification is not possible. That is designed to prevent secret interpretations such as the one that allowed bulk collection of U.S. phone records.
Does this legislation address the concerns raised by the disclosures of former NSA contractor Edward Snowden?
It addresses the most controversial program he revealed, the domestic phone records collection. But it does nothing to affect another major Snowden revelation: the NSA’s collection of foreign Internet content from U.S. tech companies, a program that sweeps up lots of American communications. And it doesn’t address the bulk of Snowden disclosures about foreign intelligence gathering and the NSA’s attempts to exploit technology, such as encryption, for the benefit of U.S. intelligence.
Who are the political winners and losers coming out of this legislative fight?
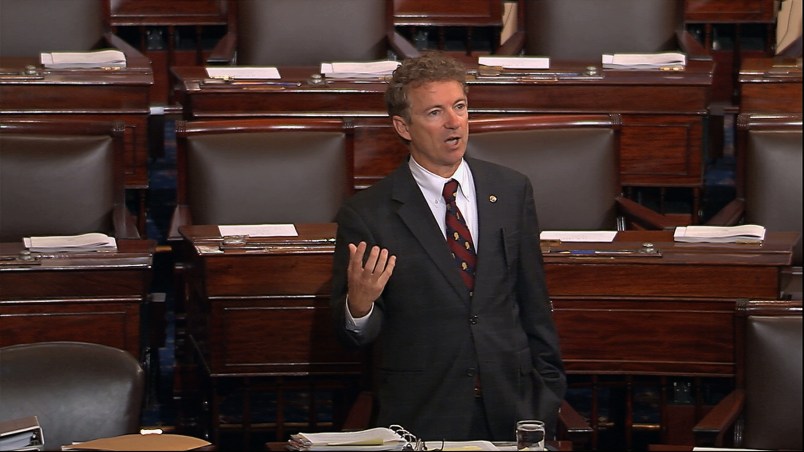
Winners include Obama, who proposed this idea more than a year ago to assuage public concerns about surveillance, and congressional Democrats, who backed it. Also coming out ahead are libertarian Republicans, including Sen. Rand Paul, R-Ky., a presidential candidate who used Senate rules to box in his own party’s leaders.
The biggest loser by any measure is Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell, R-Ky., who opposed the USA Freedom Act and thought he could force the House to accept a last-minute extension of current law. But because of Paul and others, McConnell couldn’t make that happen. He then saw his proposed changes to the USA Freedom Act defeated.
Copyright 2015 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.